The column below was used to soften hard water
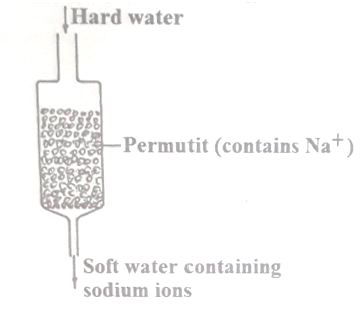
(i) Explain how hard water was soften as it passed through the column.
(ii) After sometime the material in the column is not able to soften hard water. How can the material be reactivated?
(b) Give one advantage of using hard water for domestic purposes.
Answer:
i)#Ca^(2+)# and #Mg^(2+)# ions in water are exchanged with Na+ ions in the permutit
ii)By passing a solution of concentrated sodium chloride through the column.
b)-it provides #Ca^(2+)# ions required for teeth and bornes formation.
-it coats lead pipes inside hence preventing lead poisoning in water pipes.
-it is used in brewing industries
-it is used in the formation of shells by snails.
ii)By passing a solution of concentrated sodium chloride through the column.
b)-it provides #Ca^(2+)# ions required for teeth and bornes formation.
-it coats lead pipes inside hence preventing lead poisoning in water pipes.
-it is used in brewing industries
-it is used in the formation of shells by snails.
Share To Friends Via:



 in an experiment, soap solution was added to three separate samples of water. The table below shows the volumes of the soap solutions required to form lather with #1000cm^3# of each sample of water before and after boiling.
a) Which water sample is likely to be soft? Explain.
(b) Name the cause of change in the volume of soap solution used in sample III
in an experiment, soap solution was added to three separate samples of water. The table below shows the volumes of the soap solutions required to form lather with #1000cm^3# of each sample of water before and after boiling.
a) Which water sample is likely to be soft? Explain.
(b) Name the cause of change in the volume of soap solution used in sample III