Figure 3 shows a hot water bath with metal rods inserted through one of its sides. Some wax is fixed at the end of each rod.
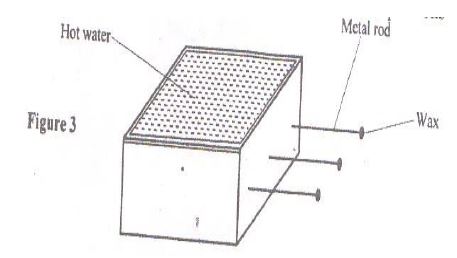
Besides the length of the rods that is kept constant, what else should be kept constant when comparing the property for the different metal rods?
Answer:
- Cross-sectional area.
Share To Friends Via:



 The control grids in a Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO) is used to control the brightness of the beam on the screen. How is this achieved?
The control grids in a Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO) is used to control the brightness of the beam on the screen. How is this achieved?