(a) In an experiment hydrogen chloride gas was prepared and reacted with aluminium
turnings to form a solid Q and gas R as shown below.
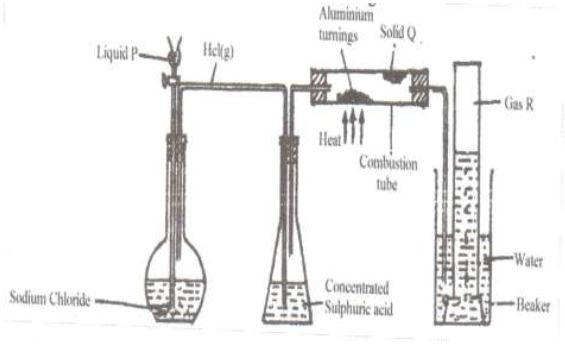
(i) Name: Liquid P
Gas R
Solid Q
(ii) Name another substance that could serve the same purpose as the concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid.
(iii) Explain the following observation. When a blue litmus paper was dipped into the water
in the beaker at the end of the experiment it turned red.
(iv) Explain why solid Q collects further away from the heated aluminium.
(b) (i) Write an equation for the reaction that takes place between ammonia gas and hydrogen
chloride gas
(ii) Calculate the mass of the product that would be formed when #200cm^3# of hydrogen chloride gas reacts completely with excess ammonia gas. (H=1.0, N=14.0, Cl=35.5, one mole of gas occupies 24 litres at room temperatures and pressure.)
Answer:
a)i)Liquid P
- Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
Solid Q
- Aluminium (III)chloride
Gas R
- Hydrogen
ii)- Anhydrous calcium chloride
iii)- The blue litmus paper turns red because the hydrogen chloride gas that does not react
with the aluminium dissolves in the water making it acidic.
iv)- Solid Q sublimes and therefore forms on the cooler part of the combustion tube away from the source of heat.
b) i) #NH_3(g)+HCl(g)rightarrowNH_4Cl(s)#
ii)#HCl(g)+NH_3(g)rightarrowNH_4Cl(s)#
moles of HCl
=#200/24000#=0.00833 moles HCl.
0.00833 moles HCl =0.00833 moles #NH_4Cl# since mole ration is 1:1
#NH_4Cl#=14+4+35.5=53.5
mass=moles x molar mass
=0.00833 x 53.5 => 0.446g.
- Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
Solid Q
- Aluminium (III)chloride
Gas R
- Hydrogen
ii)- Anhydrous calcium chloride
iii)- The blue litmus paper turns red because the hydrogen chloride gas that does not react
with the aluminium dissolves in the water making it acidic.
iv)- Solid Q sublimes and therefore forms on the cooler part of the combustion tube away from the source of heat.
b) i) #NH_3(g)+HCl(g)rightarrowNH_4Cl(s)#
ii)#HCl(g)+NH_3(g)rightarrowNH_4Cl(s)#
moles of HCl
=#200/24000#=0.00833 moles HCl.
0.00833 moles HCl =0.00833 moles #NH_4Cl# since mole ration is 1:1
#NH_4Cl#=14+4+35.5=53.5
mass=moles x molar mass
=0.00833 x 53.5 => 0.446g.
Share To Friends Via:



 in an experiment, soap solution was added to three separate samples of water. The table below shows the volumes of the soap solutions required to form lather with #1000cm^3# of each sample of water before and after boiling.
a) Which water sample is likely to be soft? Explain.
(b) Name the cause of change in the volume of soap solution used in sample III
in an experiment, soap solution was added to three separate samples of water. The table below shows the volumes of the soap solutions required to form lather with #1000cm^3# of each sample of water before and after boiling.
a) Which water sample is likely to be soft? Explain.
(b) Name the cause of change in the volume of soap solution used in sample III