With aid of a diagram, describe the structure of a coaxial cable
Answer:
1. Center Conductor:
• Lies at the heart of the cable, typically made of solid or stranded copper wire.
• Acts as the main path for carrying the electrical signal.

2. Dielectric Insulation:
• Surrounds the center conductor, often made of plastic or foam materials like polyethylene or Teflon.
• Maintains a consistent distance between the center and outer conductors.
• Prevents electrical contact between the two
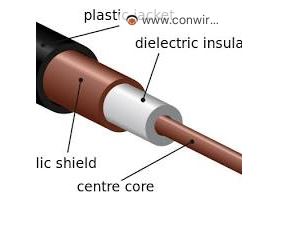
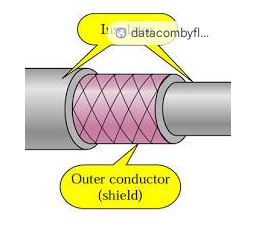
3. Outer Conductor (Shield):
• Usually a braided mesh of copper or aluminum wires woven around the dielectric.
• Acts as a shield, blocking external electromagnetic interference (EMI) from disrupting the signal within.
• Also serves as the return path for the signal, completing the circuit
4. Jacket:
• The outermost layer, typically made of PVC or another durable plastic.
• Protects the inner components from physical damage and environmental factors.

• Lies at the heart of the cable, typically made of solid or stranded copper wire.
• Acts as the main path for carrying the electrical signal.
2. Dielectric Insulation:
• Surrounds the center conductor, often made of plastic or foam materials like polyethylene or Teflon.
• Maintains a consistent distance between the center and outer conductors.
• Prevents electrical contact between the two
3. Outer Conductor (Shield):
• Usually a braided mesh of copper or aluminum wires woven around the dielectric.
• Acts as a shield, blocking external electromagnetic interference (EMI) from disrupting the signal within.
• Also serves as the return path for the signal, completing the circuit
4. Jacket:
• The outermost layer, typically made of PVC or another durable plastic.
• Protects the inner components from physical damage and environmental factors.
Share To Friends Via:



 Explain the types of transmission modes
Explain the types of transmission modes